Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Network devices use this protocol to communicate to each other and it can be used by administrators to manage the computers and network devices. It also use Application layer.
It uses UDP ports 161/162.
Working
SNMP involves one or more administrative computers called managers. They monitor and manage a group of computers.
Each of the managed computers has an agent installed that communicates with the manager.
The agent on the managed computers provides management data to the managing computer.
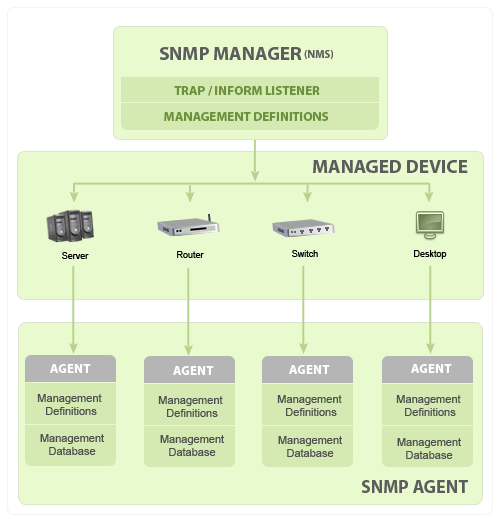
Management Information Bases or MIB is a hierarchical database which stores data exposed by the agents. Agent collects the data locally and stores it, as defined in the MIB.
It is commonly shared between the Agent and the Manager.
It contains a vast array of information on every device on the network, including users, software installed, operating systems, open ports, etc.
The MIBs comprises of managed objects identified by the name Object Identifier (Object ID or OID).
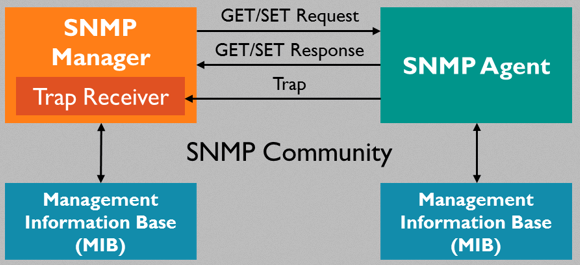
- GET: The GET operation is a request sent by the manager to the managed device. It is performed to retrieve one or more values from the managed device.
- SET: This operation is used by the managers to modify or assign the value of the Managed device.
- SNMP Traps are alert messages sent to the "SNMP manager" to notify about significant issues and events.
In short:
- Setting data to managed devices.
- Getting data from managed devices.
- Receiving events from managed devices.
SNMP Commands:
There are four types of SNMP commands used to control and monitor managed devices:
- The read command is used to monitor devices
- The write command is used to configure devices and change device settings
- The trap command is used to "trap" events from the device and report them back to the monitoring system
- Traversal operations are used to determine what variables a certain device supports
Versions
- SNMPv1 - Poor security.
The authentication of clients is in cleartext and by default, uses a "community string" that is set to "public". This community string operates like a password and it is valid for each and every node on the network.
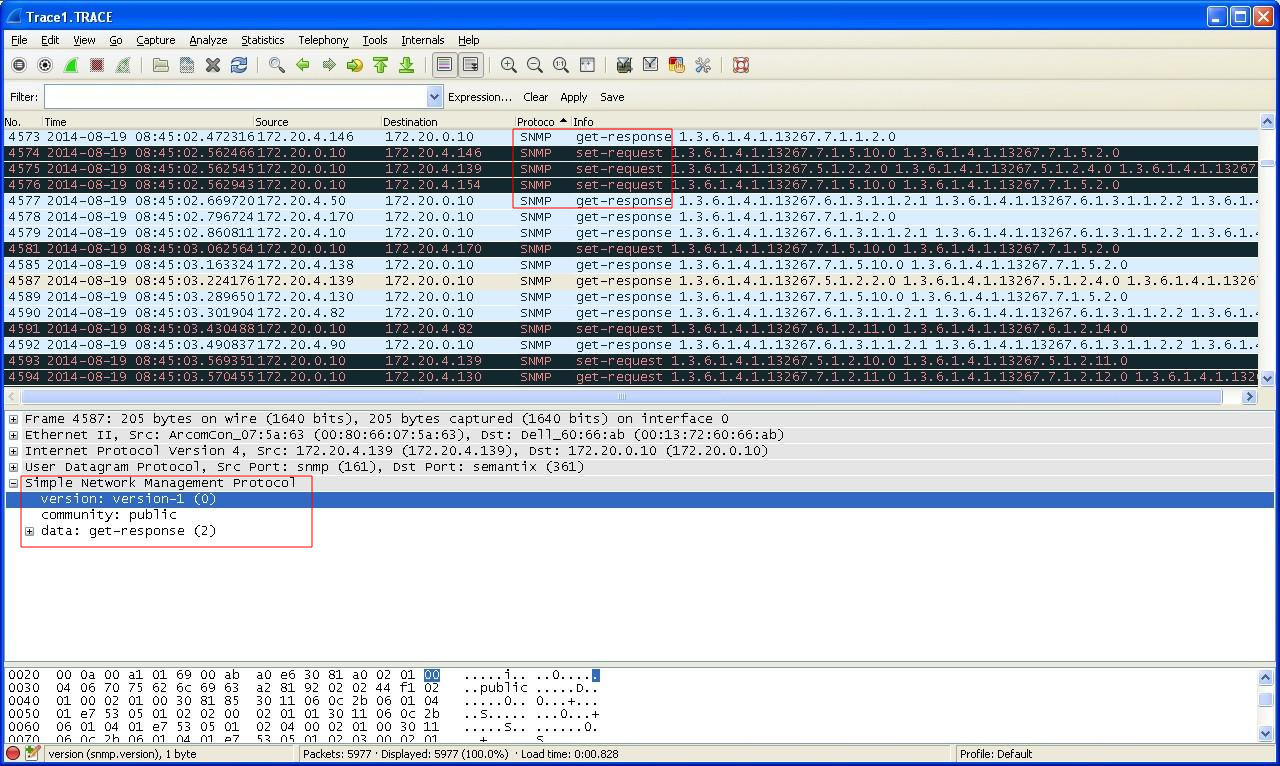
-
The authentication of the manager is also a community string and set to "private",by default.
With these strings an attacker can gather all the information from the MIB (with the public community string) and even, set the configuration on the devices (with the private community string). -
SNMPv2 - improved performance and security but it is not backwardly compatible with SNMPv1.
-
SNMPv3- more secure because it adds encryption, message integrity and authentication.